I get a daily report from my honeypots for Cowrie activity [1], which includes telnet and SSH sessions attempted on the honyepot. One indicator I use to find sessions of interest is the number of commands run. Most of the time there are about 20 commands run per session, but a session with over 1,000 commands run in a session is unexpected.
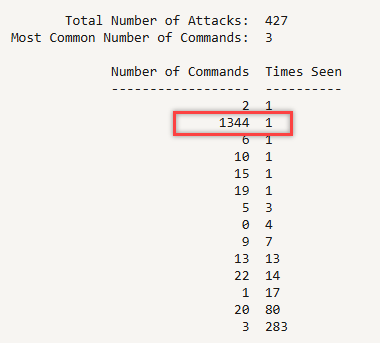
Figure 1: Summary of Cowrie [2] attacks for the day, highlighting one with a large number of commands run.
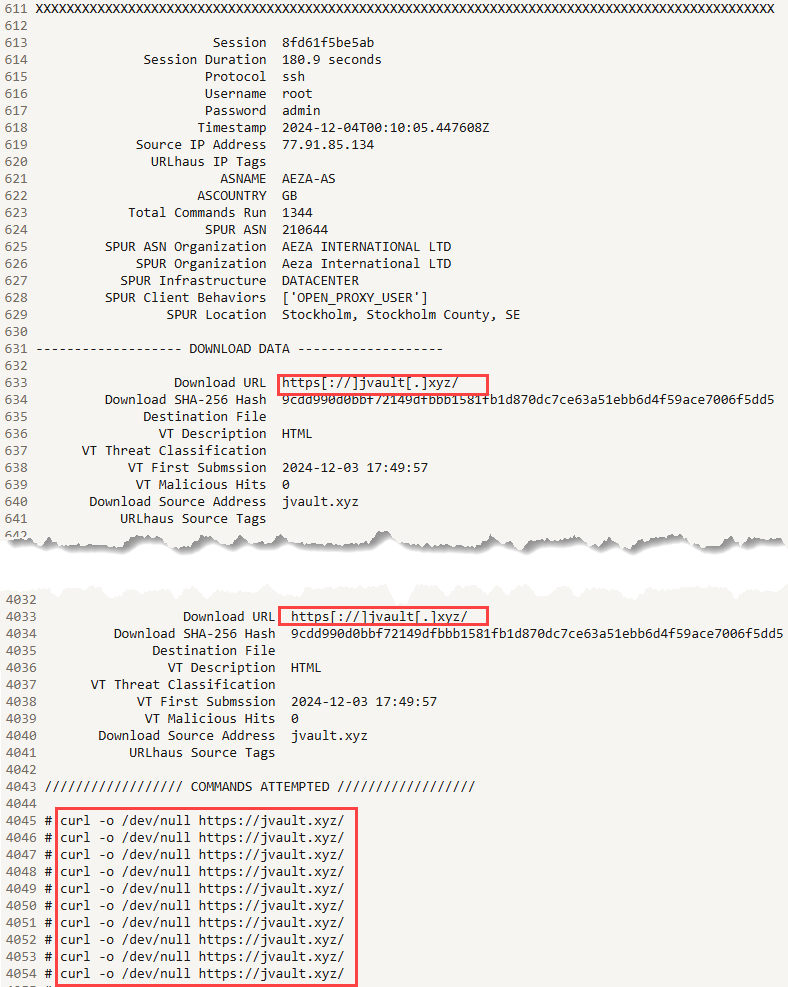
The session was only attempting to curl the website for jvault[.]xyz, but did it a total of 1,344 times in about 180 seconds for an average of 7-8 requests every second.
Figure 2: Cowrie information for repeated curl request of hxxps://jvault[.]xyz.
Why do this? Well, it could be an indicator of an attempted DDoS attack if performing this kind of activity across a large number of systems. Was there something about this website that was of interest? It appears that the website is related to cyptocurrency. The main page mentions staking [3], DeFi [4], Launchpads [5] and DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) [6].
Figure 3: Homepage screenshot of hxxps://jvault[.]xyz.
A couple of days since this initial finding, there were similar sessions that also tried to curl various websites. I used JQ with some raw logs on my honeypots to find similar activity.
# read cowrie JSON files
# cat /logs/cowrie.json*
# select any data from source IP 77.91.85.134
# jq 'select(.src_ip=="77.91.85.134")'
# select any data with the 'input' key present (commands run on honeypot)
# jq 'select(.input)'
# extract timestamp, source IP and command from logs returned
# jq '{timestamp, src_ip, input}'
# select elements of array and display in TSV (tab separated value) format
# jq -r '[.[]] | @tsv'
# sort alphabetically
# sort
# display first 10 items
# head
cat /logs/cowrie.json* | jq 'select(.src_ip=="77.91.85.134")' | jq 'select(.input)'
| jq '{timestamp, src_ip, input}' | jq -r '[.[]] | @tsv' | sort | head
# output from GCP honeypot
2024-11-18T19:10:19.721578Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://sambot[.]ru
2024-11-18T19:10:19.860960Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://sambot[.]ru
2024-11-18T19:10:19.903455Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://sambot[.]ru
2024-11-18T19:10:20.098534Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://sambot[.]ru
2024-11-18T19:10:20.228898Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://sambot[.]ru
2024-11-18T19:10:20.282748Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://sambot[.]ru
2024-11-18T19:10:20.583350Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://sambot[.]ru
2024-11-18T19:10:20.636637Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://sambot[.]ru
2024-11-18T19:10:20.978894Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://sambot[.]ru
2024-11-18T19:10:21.022589Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://sambot[.]ru
# output from Azure honeypot
2024-11-21T15:29:18.127274Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://jambler[.]io
2024-11-21T15:29:18.282875Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://jambler[.]io
2024-11-21T15:29:18.499913Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://jambler[.]io
2024-11-21T15:29:18.744135Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://jambler[.]io
2024-11-21T15:29:18.894551Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://jambler[.]io
2024-11-21T15:29:19.257191Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://jambler[.]io
2024-11-21T15:29:19.404682Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://jambler[.]io
2024-11-21T15:29:19.900103Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://jambler[.]io
2024-11-21T15:29:20.171343Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://jambler[.]io
2024-11-21T15:29:20.594296Z 77.91.85.134 curl -o /dev/null https://jambler[.]io
# read cowrie JSON files
# cat /logs/cowrie.json*
# select any data from source IP 77.91.85.134
# jq 'select(.src_ip=="77.91.85.134")'
# select any data with the 'input' key present (commands run on honeypot)
# jq 'select(.input)'
# extract timestamp, source IP and command from logs returned
# jq '{timestamp, src_ip, input}'
# select elements of array and display in TSV (tab separated value) format
# jq -r '[.[]] | @tsv'
# get third value per line (command in this case)
# cut -f 3
# sort alphabetically
# sort
# give counts per command found
# uniq -c
# sort results by count, ascending
# sort -n
cat /logs/cowrie.json* | jq 'select(.src_ip=="77.91.85.134")' | jq 'select(.input)'
| jq '{timestamp, src_ip, input}' | jq -r '[.[]] | @tsv' | cut -f 3 | sort | uniq -c
| sort -n
#output from GCP honeypot
1 curl -s -A "myuser" https://eth0[.]me
79 curl -o /dev/null https://token-mining[.]org:443
1035 curl -o /dev/null https://exchange-pool[.]com/
1201 curl -o /dev/null http://193.222.99[.]121
1244 curl -o /dev/null https://botman[.]pro
1348 curl -o /dev/null https://umbrella[.]day/
1452 curl -o /dev/null https://niolic[.]com
1506 curl -o /dev/null https://steam-up[.]ru
1594 curl -o /dev/null http://stk-ms[.]ru
1764 curl -o /dev/null http://85.217.171[.]107:443
1773 curl -o /dev/null https://bottap[.]ru/
1867 curl -o /dev/null https://sambot[.]ru
2282 curl -o /dev/null https://santasol[.]fun/
2361 curl -o /dev/null https://static.tgcube[.]store/
3296 curl -o /dev/null https://baboon-tg-web-app-v2.onrender[.]com
4314 curl -o /dev/null https://mystars-hk.syllix[.]io
4633 curl -o /dev/null https://btcbot[.]cc
5699 curl -o /dev/null https://www.gogetsms[.]com/
6179 curl -o /dev/null https://tgmaster[.]xyz
#output from Azure honeypot
638 curl -o /dev/null https://freeapi.bot-t[.]com/
1375 curl -o /dev/null https://jambler[.]io
1626 curl -o /dev/null https://duda.com[.]ua/
3876 curl -o /dev/null https://app.tbiz[.]pro
4195 curl -o /dev/null https://www.gift-bnb[.]org/
7759 curl -o /dev/null https://jvault[.]xyz/
15743 curl -o /dev/null https://tgmaster[.]xyz
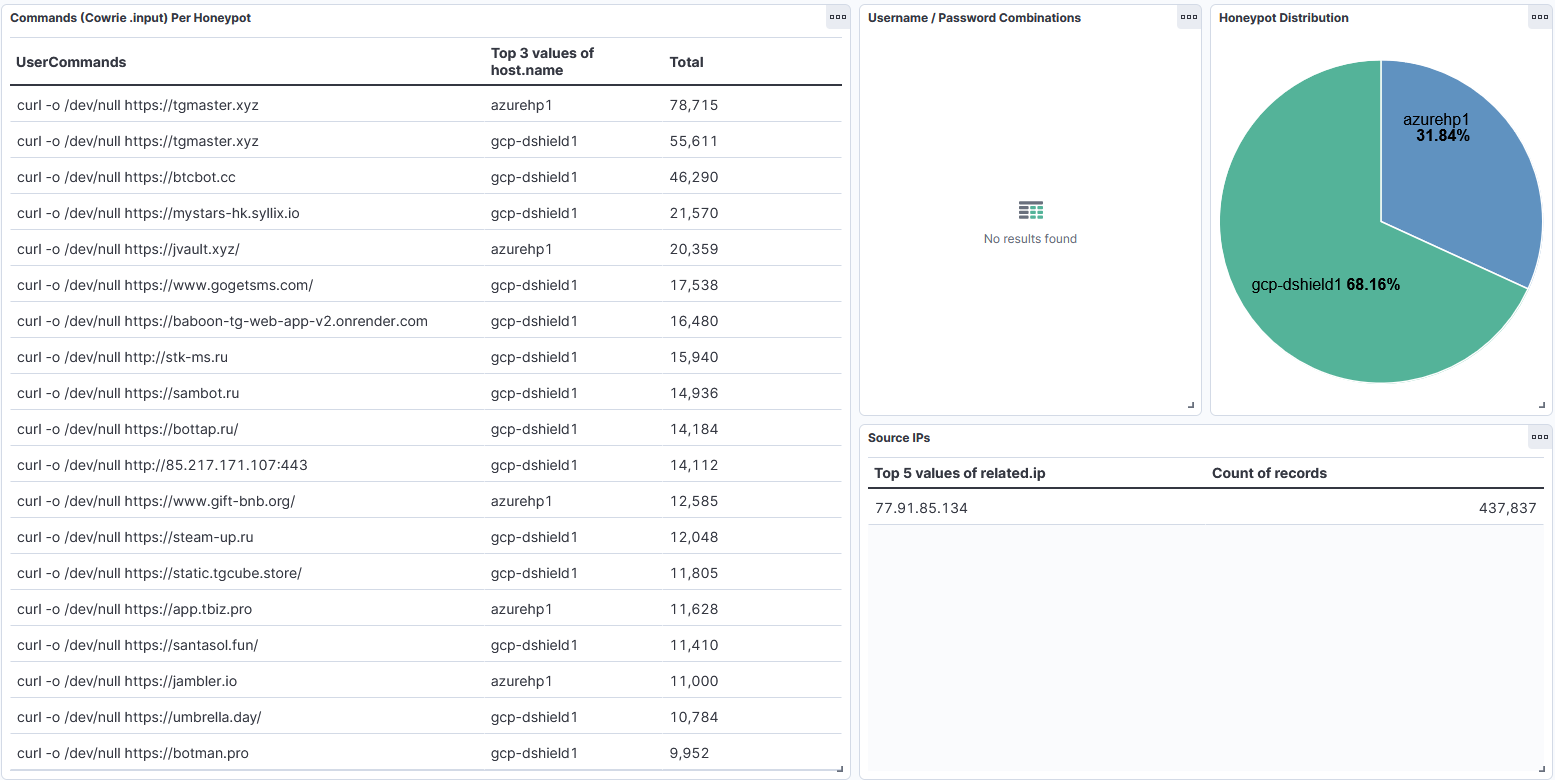
There were many other sessions with similar activity, using curl repeatedly for a website, all coming from the same source IP of %%ip:77.91.85.134%%. There were also many more websites than expected. Since I regularly backup and prune my local honeypot logs, I went to my DShield-SIEM [7] instance to build a dashboard to try and get some additional information.
Figure 4: Results for commands run during Cowrie sessions from %%ip:77.91.85.134%%.
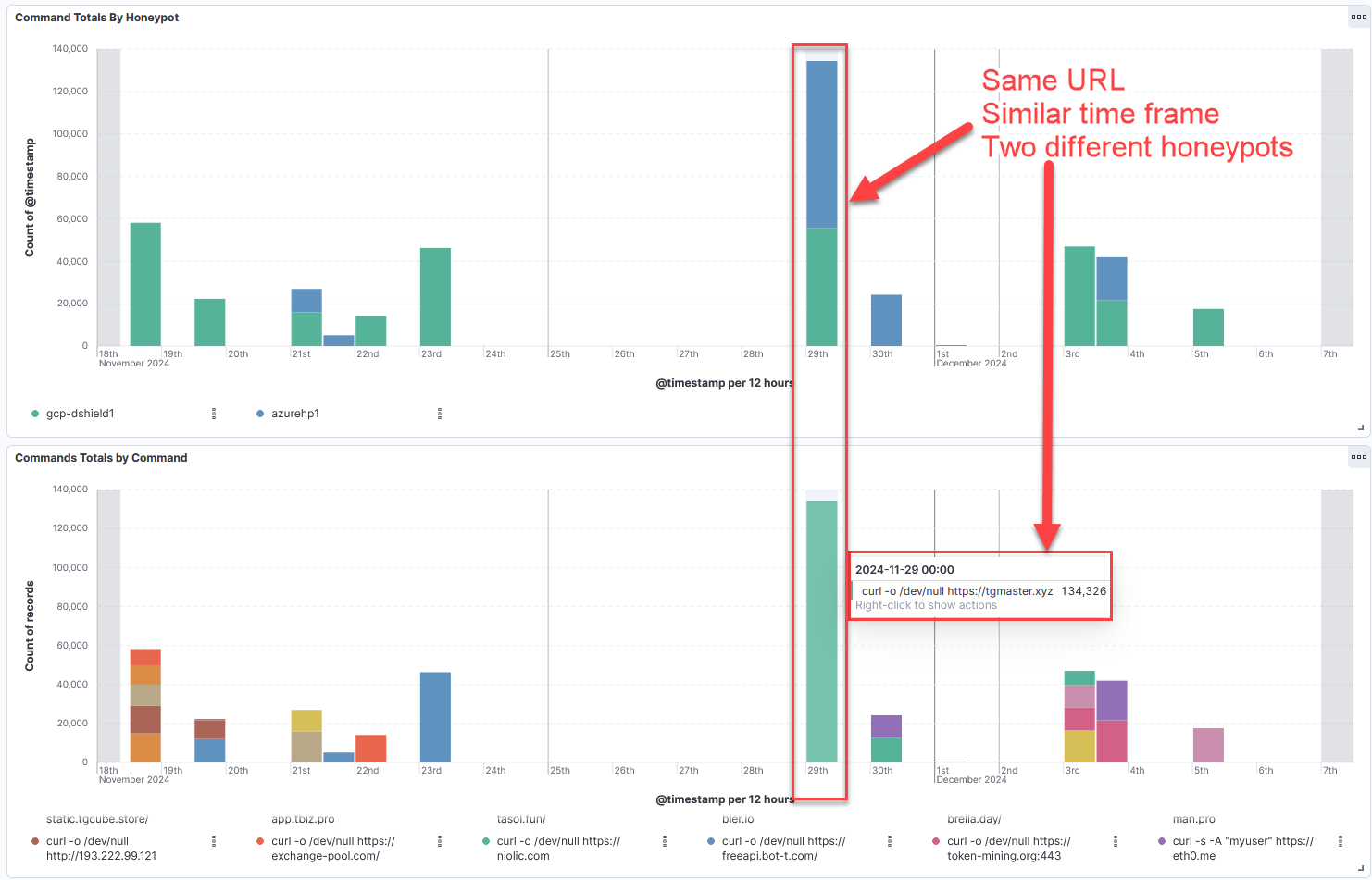
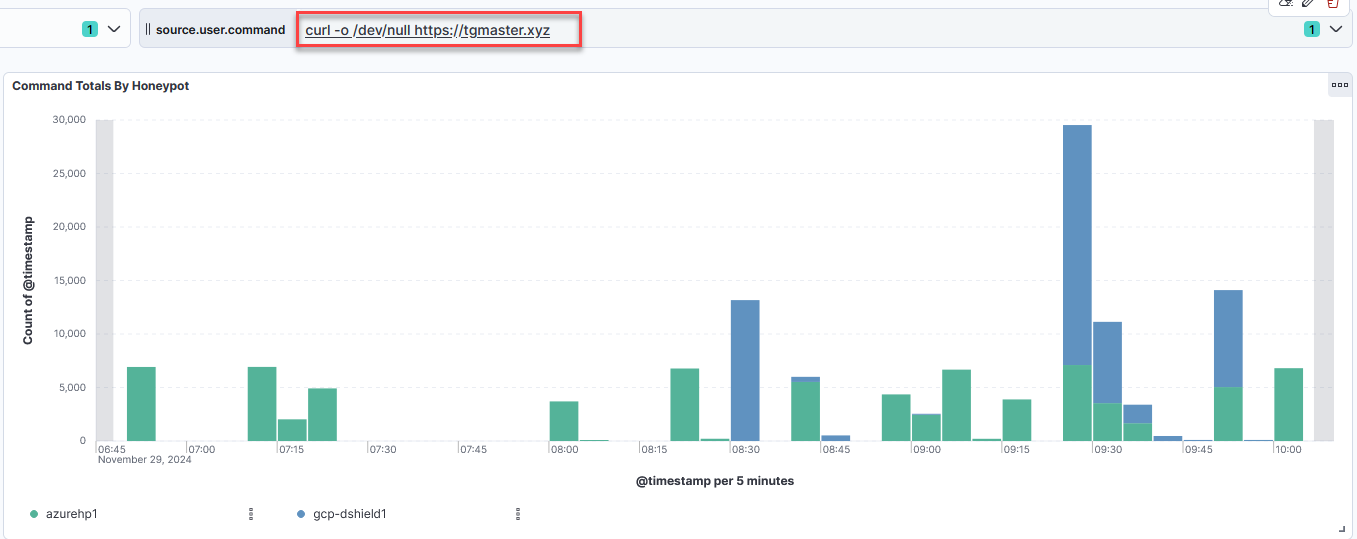
Figure 5: Comparison of command volume and honeypot volume, highlighting one curl command that was running from two honeypots in the same timeframe.
An interesting item is activity for one website happening at the same time between two honeypots.
Figure 6: Activity from two honeypots asked to execute a curl command for tgmaster[.]xyz within a 3-4 hour timeframe.
The data was exporrted from the dashboard and the websites were manually reviewed to try and identify a general purpose. In many cases the websites were in Russian and Google Translate [8] was used to read the information. In a couple instances, the websites were also restricted by location, so a VPN was used to access the content from a Russian geolocated IP address.
| Total Honeypot Requests | Site | Manual Review | GeoIP Restricted |
|---|---|---|---|
| 134,326 | https://tgmaster[.]xyz | Telegram Bot Construction | No |
| 46,290 | https://btcbot[.]cc | Sales Bots / Telegram | No |
| 21,570 | https://mystars-hk[.]syllix[.]io | MyStars Telegram Bot | Yes |
| 20,359 | https://jvault[.]xyz/ | Cryptocurrency / JetTon Staking | No |
| 17,538 | https://www[.]gogetsms[.]com/ | SMS / Temporary Numbers | No |
| 16,480 | https://baboon-tg-web-app-v2[.]onrender[.]com | Telegram Bots / Crytocurrency | No |
| 15,940 | http://stk-ms[.]ru | Building Construction Design | No |
| 14,936 | https://sambot[.]ru | Telegram Bot Construction | No |
| 14,184 | https://bottap[.]ru/ | Designer Chatbots | No |
| 14,112 | http://85[.]217[.]171[.]107:443 | “NeoVPN” (keys[.]neovpn[.]online) / Mention of bots to add money, may be cryptocurrentcy related | No |
| 12,585 | https://www[.]gift-bnb[.]org/ | BBAPool / Cryptocurrency Bots | No |
| 12,048 | https://steam-up[.]ru | Steam Balance Replenishment | No |
| 11,805 | https://static[.]tgcube[.]store/ | MARKETSSUPER | No |
| 11,628 | https://app[.]tbiz[.]pro | Trading Bots | Yes |
| 11,410 | https://santasol[.]fun/ | Mobile Game | No |
| 11,000 | https://jambler[.]io | Cryptocurrency / Bitcoin mixing | No |
| 10,784 | https://umbrella[.]day/ | Website and Bot Creation | No |
| 9,952 | https://botman[.]pro | Chatbot Creation | No |
| 9,608 | http://193[.]222[.]99[.]121 | Token Mining (token-mining[.]org) / MNG LAB | No |
| 8,280 | https://exchange-pool[.]com/ | Cryptocurrency Exchange | No |
| 7,260 | https://niolic[.]com | Cryptocurrency / Investments | No |
| 5,104 | https://freeapi[.]bot-t[.]com/ | Telegram Bots | No |
| 632 | https://token-mining[.]org:443 | Token Mining (token-mining[.]org) / MNG LAB | No |
| 6 | https://eth0[.]me | Uknown (returns visitor IP address) | No |
Figure 6: Webites from curl commands, number of times accessed and website purpose from manual review.
There is a general theme to the websites, including:
- Bot construction
- Communication platforms
- Cryptocurrency
Since collecting the original data, a couple new sites have been seen being accessed in a similar way:
https://duda[.]com[.]ua/– smoking-related sales websitehttps://178.159.43[.]149– cerficate forexpress12[.]comdomain, which redirects tohttps://t[.]me/durov(provides link to view “Thoughts from the CEO of Telegram” in Telegram)
From my collection of honeypots, these curl commands have only been seen originating from %%ip:77.91.85.134%% and the commands start with “curl -o /dev/null“. The activity started on November 18, 2024 and new activity is still being seen.
[1] https://github.com/jslagrew/cowrieprocessor
[2] https://github.com/cowrie/cowrie
[3] https://www.coinbase.com/learn/crypto-basics/what-is-staking
[4] https://www.coinbase.com/learn/crypto-basics/what-is-defi
[5] https://cointelegraph.com/news/what-is-a-crypto-launchpad-and-how-does-it-work
[6] https://www.investopedia.com/tech/what-dao/
[7] https://github.com/bruneaug/DShield-SIEM
[8] https://translate.google.com/?sl=auto&tl=en&op=translate
—
Jesse La Grew
Handler
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
Discover more from Cyber GRC Hive
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.